
N.C. OCME Annual Report 1993
Back to Annual Report Index | Chapter 3
Chapter 2: All Medical Examiner Cases
The medical examiner system became statewide in North Carolina during the early 1970's. Into the mid-1980’s, there was an absolute decrease in the number of deaths investigated by the system; this occurred in spite of an increase in the total number of deaths in the state as well as an increase in total population base. Since 1984, however, this trend reversed and the number of deaths investigated by the system has increased. Four categories of death that have shown major changes over that period include natural deaths, homicides, motor vehicle accidents, fires, and drowning (Table 1).
The absolute number of natural deaths investigated yearly remained relatively constant through 1981. In 1982 there was a drop of approximately 12 percent and this lower number has been maintained. This decrease in the number of natural deaths investigated may indicate that a greater percent of North Carolinians are dying in hospitals, or nursing homes or that more deaths occurring at home are being certified by attending physicians rather than being referred to the medical examiner system.
Until recently, the absolute number of homicides, as well as homicide rates, decreased almost on a regular basis. From 1983-1988, the rate of homicide seemed stabilized. However, 1989 produced an unwelcome 17 percent increase in the rate, followed by increases again in 1990 and 1991. In 1992, the homicide rate declined slightly from 1991 levels, but the rate returned to higher levels in 1993.
The number of motor vehicle accident deaths certified through the system in 1972 and 1973 was around 1,900 deaths. This was followed in 1974, by a striking drop in the absolute number and rate. For the next seven years, the absolute number remained relatively constant (around 1,500 deaths) though the rate dropped slightly. The years 1982 and 1983 showed the lowest absolute numbers and rates, but 1984 and 1985 saw an increase. In 1986, the total number of deaths reached 1,700 with an increase in the rate to that of the mid 1970's. From 1987 through 1992, the number of motor vehicle related deaths (along with the rate) has steadily declined. Both the number and rate of these deaths increased again in 1993. Other categories of death have shown relatively little change although the number and rate of drownings have both declined fairly steadily. The suicide rate has remained relatively constant, though the absolute numbers have increased yearly. Falls have also remained relatively constant.
Table 1: 1972-1993 Medical Examiner Cases and Case Rates/100,000 Population by Manner of Death and Accidental Causes
| YEAR | TOTAL | NATURAL | HOMICIDE | SUICIDE | MOTOR VEHICLE | FIRE | FALL | DROWNING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 | 9,304 | 4,517 | 792 (15.0) | 646 (12.2) | 1,932 (36.5) | 217 (4.1) | 143 (2.7) | 236 (4.5) |
| 1972 | 9,304 | 4,517 | 792 (15.0) | 646 (12.2) | 1,932 (36.5) | 217 (4.1) | 143 (2.7) | 236 (4.5) |
| 1973 | 9,879 | 4,944 | 847 (15.7) | 726 (13.5) | 1.920 (35.7) | 213 (4.0) | 183 (3.4) | 288 (5.3) |
| 1974 | 9,157 | 4,588 | 804 (14.7) | 706 (12.9) | 1,582 (29.0) | 188 (3.4) | 169 (3.1) | 230 (4.2) |
| 1975 | 9,089 | 4,516 | 828 (15.0) | 764 (13.8) | 1,535 (27.7) | 187 (3.4) | 175 (3.2) | 281 (5.1) |
| 1976 | 8,902 | 4,545 | 734 (13.1) | 690 (12.3) | 1,590 (28.4) | 218 (3.9) | 160 (2.9) | 229 (4.1) |
| 1977 | 9,128 | 4,679 | 683 (12.0) | 759 (13.4) | 1,524 (26.9) | 238 (4.2) | 176 (3.1) | 270 (4.8) |
| 1978 | 8,973 | 4,622 | 704 (12.3) | 691 (12.0) | 1,578 (27.5) | 229 (4.1) | 174 (3.0) | 210 (3.7) |
| 1979 | 8,883 | 4,561 | 700 (12.1) | 737 (12.7) | 1,558 (26.8) | 214 (3.7) | 133 (2.3) | 155 (2.7) |
| 1980 | 9,097 | 4,701 | 721 (12.2) | 682 (11.6) | 1,570 (26.6) | 195 (3.3) | 189 (3.2) | 238 (4.0) |
| 1981 | 8,874 | 4,657 | 643 (10.8) | 777 (13.0) | 1,560 (26.2) | 258 (4.3) | 158 (2.7) | 148 (2.5) |
| 1982 | 8,085 | 4,075 | 640 (10.6) | 817 (13.6) | 1,387 (23.1) | 197 (3.3) | 154 (2.6) | 146 (2.4) |
| 1983 | 7,949 | 4,089 | 568 (9.3) | 771 (12.7) | 1,315 (21.6) | 192 (3.2) | 177 (2.9) | 187 (3.1) |
| 1984 | 7,888 | 3,842 | 534 (8.7) | 828 (13.4) | 1,521 (24.7) | 167 (2.7) | 172 (2.8) | 182 (3.0) |
| 1985 | 7,964 | 3,796 | 585 (9.4) | 803 (12.8) | 1,554 (24.8) | 218 (3.5) | 194 (3.1) | 162 (2.6) |
| 1986 | 8,245 | 3,903 | 598 (9.4) | 794 (12.5) | 1,743 (27.6) | 231 (3.6) | 174 (2.7) | 152 (2.4) |
| 1987 | 8,421 | 4,127 | 598 (9.3) | 800 (12.5) | 1,690 (26.4) | 198 (3.1) | 201 (3.1) | 156 (2.4) |
| 1988 | 8,715 | 4,314 | 619 (9.5) | 811 (12.5) | 1,676 (25.8) | 209 (3.2) | 201 (3.1) | 179 (2.8) |
| 1989 | 8,543 | 4,093 | 730 (11.1) | 894 (13.6) | 1,600 (24.4) | 201 (3.1) | 187 (2.8) | 151 (2.3) |
| 1990 | 8,449 | 3,989 | 818 (12.3) | 971 (14.6) | 1,500 (22.6) | 154 (2.3) | 210 (3.2) | 149 (2.2) |
| 1991 | 8,402 | 3,994 | 920 (13.6) | 849 (12.6) | 1,458 (21.6) | 168 (2.5) | 234 (3.5) | 163 (2.4) |
| 1992 | 8,309 | 4,109 | 829 (12.1) | 889 (13.0) | 1,381 (20.2) | 175 (2.6) | 223 (3.3) | 126 (1.8) |
| 1993 | 8,613 | 4,094 | 953 (13.7) | 878 (12.6) | 1,513 (21.8) | 164 (2.4) | 247 (3.6) | 133 (1.9) |
Falls are the one category of unnatural death that tends to be underreported in ME statistics, due in large part to the often protracted time from injury to death as a result of complications from the actual injury, especially among elderly patients.
Figure 1 shows that in 1993, natural causes accounted for the largest percentage of cases, followed by motor vehicle and other accidents. A majority of the cases (94%) were known to be North Carolina residents. Other states contributing the most to North Carolina's caseload were Virginia (114), South Carolina (99), and Florida (61).
Figure 1
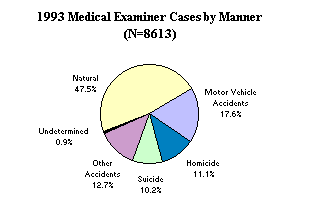
Table 2 shows the percentage of Medical Examiner cases by race and sex. Comparing this to the percentage of all North Carolina deaths by race and sex, Table 3 shows that white and nonwhite males are overrepresented in Medical Examiner cases while white females are underrepresented.
Table 2: 1993 Percentage of Medical Examiner Cases by Race and Sex
| White | Nonwhite | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 46.8 | 23.9 | 70.7 |
| Female | 19.1 | 10.2 | 29.3 |
| Total | 65.9 | 34.1 | 100.0 |
Table 3: 1993 Percentage of All NC Deaths Cases by Race and Sex
| White | Nonwhite | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 39.3 | 13.1 | 52.4 |
| Female | 36.8 | 10.9 | 47.7 |
| Total | 76.1 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
Autopsies
Autopsies were ordered in approximately 44 percent of Medical Examiner cases in 1993. The percentage of cases autopsied by manner were 40 percent for natural deaths, 99 percent for homicides, 33 percent for suicides, 19 percent for motor vehicle accidents, 49 percent for other accidents, and 93 percent for undetermined deaths.
Toxicology
Toxicology testing was performed on approximately 88 percent of Medical Examiner cases in 1993. The majority of those tests were for ethanol, but the toxicology lab also tests for more than 100 other drugs and chemicals. Table 4 summarizes deaths due to drugs for the 1993. Figure 2 shows Medical Examiner cases by manner and alcohol levels. For those tested, alcohol was most prevalent in homicides, but alcohol was a factor in a disturbing number of other types of deaths. Note: 100mg/dl is the equivalent of 0.10 percent blood alcohol.
Figure 2
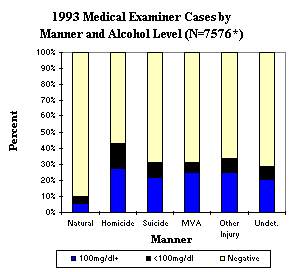
*Number of cases tested
Table 4: Medical Examiner Deaths Due to Drugs or Poisons, 1993
| Substance | Number of Deaths |
|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | 5 |
| Alcohol | 55 |
| Alcohol and Other Drugs | 13 |
| Antidepressants | 43 |
| Barbiturates | 3 |
| Carbon Monoxide | 45 |
| Cocaine | 34 |
| Codeine | 2 |
| Morphine | 21 |
| Multiple Drug Toxicity | 30 |
| Other Drugs | 42 |
| Propoxyphene | 5 |
| Salicylates | 3 |
| Therapeutic Drug Reaction | 12 |
| Total | 313 |
The percentages of cases that were not tested because an adequate specimen was not available include, by manner: 15 percent for natural deaths; 4 percent for homicides; 10 percent for suicides; 16 percent for motor vehicle accidents; 21 percent for other accidents; and 22 percent for undetermined deaths. Other reasons some cases were not tested include: young age of the victim; prolonged survival time after injury; and decomposition.
Years of Life Lost
Because deaths due to violence (external causes) disproportionately affect the younger segments of our population, it is important to consider not only the total number of lives lost, but also the years of potential life lost. Table 5 exhibits the potential years of life lost for selected causes of death in 1993. The table was computed by calculating the difference between the age at death and the appropriate race-sex specific life expectancy at birth. therefore, the potential years of life lost are the number of years that were not lived because of a premature death. In 1993, approximately 138,000 potential years of life were lost because of homicides, suicides, accidents, and other external causes in North Carolina. This is an average of 31 potential years of life lost per death, and it shows the premature nature of these deaths. Motor vehicle accident deaths have the highest number of potential years of life lost per death (35.5) followed by homicides (34.6) and suicide (26.1). In comparison, the potential years of life lost per death from heart disease and cancer, the two leading causes of death in North Carolina for 1989, are 4.5 and 7.5, respectively.
Although approximately eight times as many people die yearly in North Carolina from the two leading causes of death (heart disease and cancer) than die from trauma, when viewed in terms of total years of potential life lost the overall toll is much closer--200,000 vs. 138,000 years respectively.
Table 5: 1993 North Carolina Deaths by Manner/Cause of Death and Potential Years of Life Lost
| Total Number of Deaths | Potential Years of Life Lost | Potential Years of Life Lost/Death | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homicide | 953 | 32,995 | 34.6 |
| Suicide | 878 | 22,939 | 26.1 |
| Motor Vehicle Accidents | 1,513 | 53,711 | 35.5 |
| Fires | 164 | 3,564 | 21.7 |
| Falls | 247 | 2,562 | 10.4 |
| Other External Causes | 962 | 21,845 | 22.7 |
| Heart Disease | 19,832 | 89,059 | 4.5 |
| Cancer | 14,778 | 111,375 | 7.5 |
| All Manner / Causes | 64,354 | 565,121 | 8.8 |
"Years of Life Lost" is expected years of life remaining, comparing the decedent’s age at death to the race-sex specific life expectancy at birth. Life expectancies from the 1979 North Carolina Life Table are as follows: White Males = 70, White Females = 79, Nonwhite Males = 64, Nonwhite Females = 73. Total deaths for homicide, suicide, motor vehicle accidents, fires, falls and other external causes are from the Medical Examiner Information System Database. Total deaths from heart disease and cancer as well as all manner/causes are from the Vital Records Database.